Delta Connections
Three-phase transformers are used when three-phase power
is required for larger loads such as industrial motors. There
are two basic three-phase transformer connections, delta and
wye. Delta transformers are used where the distance from
the supply to the load is short. A delta is like three single phase
transformers connected together. The secondary of a
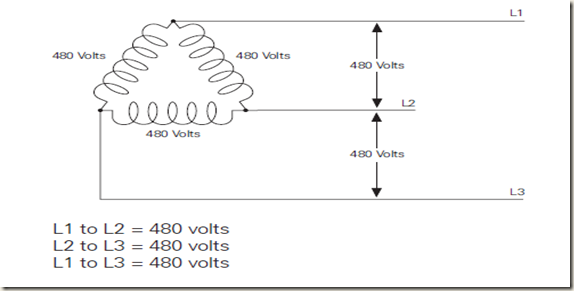
delta transformer is illustrated below. For simplicity, only the
secondary of a three-phase transformer is shown. The voltages
shown on the illustration are secondary voltages available
to the load. Delta transformers are schematically drawn in a
triangle. The voltages across each winding of the delta triangle
represents one phase of a three phase system. The voltage is
always the same between any two wires. A single phase (L1 to
L2) can be used to supply single phase loads. All three phases
are used to supply three phase loads
Balanced Delta Current
When current is the same in all three coils, it is said to be
balanced. In each phase, current has two paths to follow. For
example, current flowing from L1 to the connection point at
the top of the delta can flow down through one coil to L2, and
down through another coil to L3. When current is balanced, coil
current is 58% of the line current measured on each phase. If
the line current is 50 amps on each phase, coil current would be
29 amps
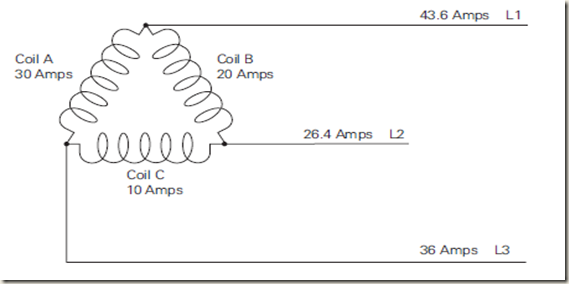
Unbalanced Delta Current
When current is different in all three coils, it is unbalanced. The
following diagram depicts an unbalanced system
Though current is usually measured with an ammeter, line current
of an unbalanced delta transformer can be calculated with
the following formulas
Wye Connections
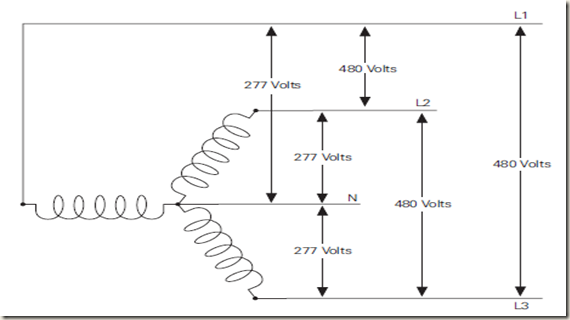
The wye connection is also known as a star connection. Three
transformers are connected to form a “Y” shape. The wye
transformer secondary, (shown below) has four leads, three
phase connectors, and one neutral. The voltage across any
phase (line-to-neutral) will always be less than the line-to-line
voltage. The line-to-line voltage is 1.732 times the line-to-neutral
voltage. In the circuit below, line-to-neutral voltage is 277 volts.
Line-to-line voltage will be 480 volts (277 x 1.732)


No comments:
Post a Comment